vEM reveals the cellular composition of the Blood Nerve Barrier
Posted by Mario Elias Ortega Sandoval, on 11 October 2024
by Giulia Casal*, Ian White*, Jemima Burden* & Alison C. Lloyd*
*Laboratory for Molecular Cell Biology, University College London, UK
Challenge
The blood barriers of the nervous system are essential for protecting neural tissues and maintaining homeostasis. While the blood-brain barrier (BBB) of the central nervous system (CNS) is well characterized, comprising a monolayer of endothelial cells supported by nearly complete pericyte and astrocyte coverage, there is a lack of comparable understanding in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
In the CNS, the microenvironment of the BBB is critical for its barrier properties1. However, the structure and regulation of the blood-nerve barrier (BNB) in the PNS remain poorly understood. The BNB plays a crucial role in PNS function, yet its vascular component (EndoVs) and its cellular composition have not been described to date, despite the importance of the BNB for PNS function, with disruption associated with disorders such as diabetes and neuropathies2,3.
Technique: AT-SEM
Array Tomography-SEM (AT-SEM)5 provides 3D ultrastructural information about a sample by sequentially imaging a region of interest (ROI) in a series of ultrathin sections of that sample. The sections are cut from a heavy metal stained and resin embedded sample, and are collected in series order onto a solid conductive substrate such as silicon wafer or ITO coated coverslip for imaging in the SEM5.
The resulting data stack can then be analysed for 3D information such as surface areas, blood vessel coverage and the extent of cell to cell interactions. Unlike other vEM techniques AT-SEM is non destructive so samples can be reinterrogated as often as required, at different resolutions and multiple ROI imaged. AT-SEM is particularly useful when following structures that meander through a sample, e.g. blood vessels, as their locations are visible at the onset of imaging and can be easily tracked.

Research
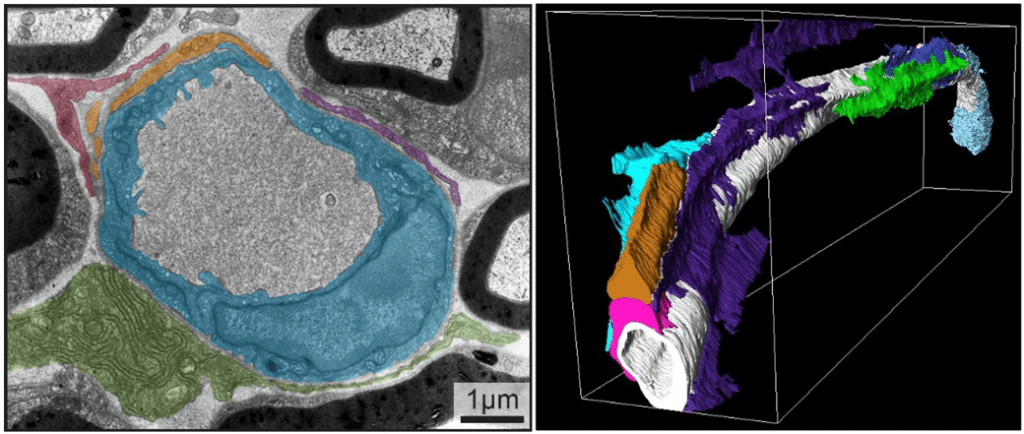
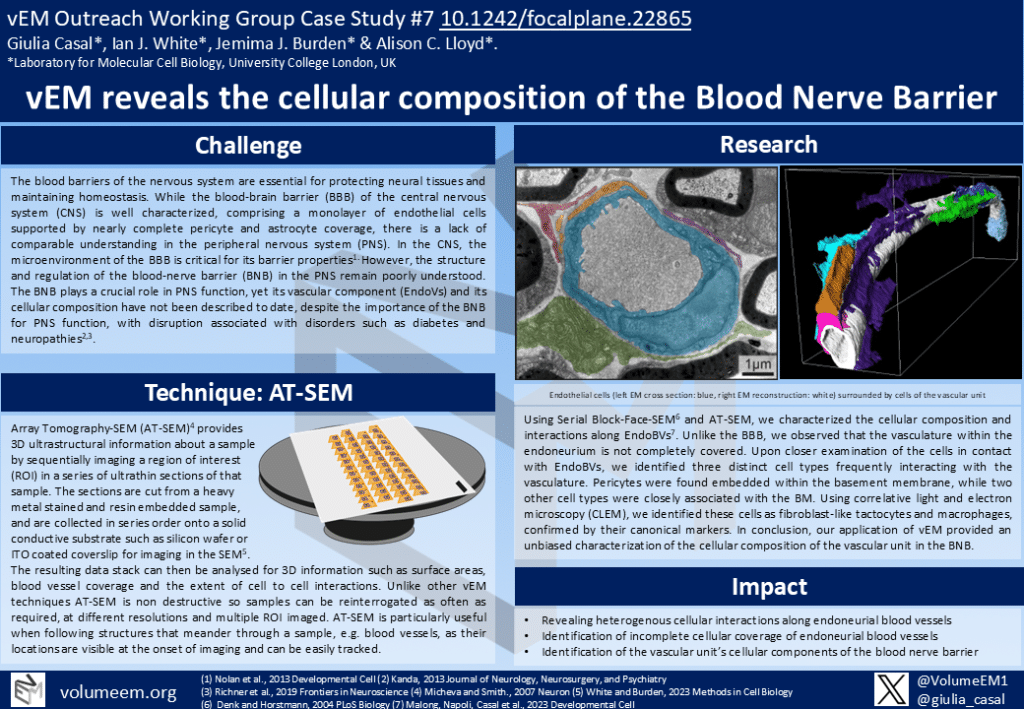
Using Serial Block-Face-SEM6 and AT-SEM, we characterized the cellular composition and interactions along EndoBVs7. Unlike the BBB, we observed that the vasculature within the endoneurium is not completely covered. Upon closer examination of the cells in contact with EndoBVs, we identified three distinct cell types frequently interacting with the vasculature. Pericytes were found embedded within the basement membrane, while two other cell types were closely associated with the BM.
Using correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM), we identified these cells as fibroblast-like tactocytes and macrophages, confirmed by their canonical markers. In conclusion, our application of vEM provided an unbiased characterization of the cellular composition of the vascular unit in the BNB.

Impact
•Revealing heterogenous cellular interactions along endoneurial blood vessels
•Identification of incomplete cellular coverage of endoneurial blood vessels
•Identification of the vascular unit’s cellular components of the blood nerve barrier
References
(1) Nolan et al., 2013 Developmental Cell
(2) Kanda, 2013 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry
(3) Richner et al., 2019 Frontiers in Neuroscience
(4) Micheva and Smith., 2007 Neuron
(5) White and Burden, 2023 Methods in Cell Biology
(6) Denk and Horstmann, 2004 PLoS Biology
(7) Malong, Napoli, Casal et al., 2023 Developmental Cell
Poster


 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)