Featured image with Seth Agyei Domfeh
Posted by FocalPlane, on 20 June 2025
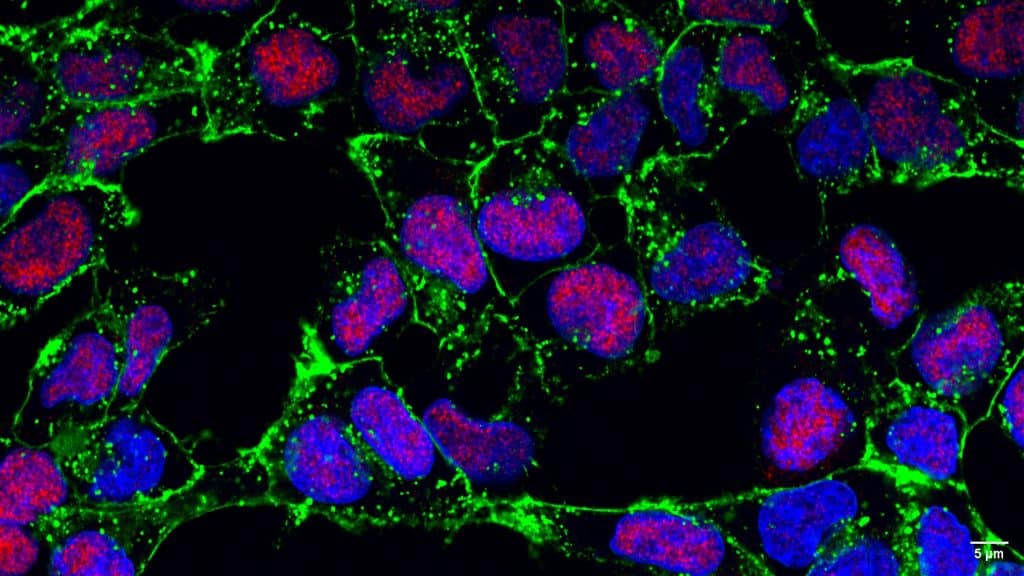
Our featured image, acquired by Seth Agyei Domfeh, shows the nuclear localisation of interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells stimulated with interferon α (IFN-α).
HepG2 cells were cultured on a poly-D-lysine-coated coverslip for 24 hours and stimulated with 1000 IU/ml IFN-α. At 24 hours post-stimulation, the cells were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde, non-specific binding sites blocked with 2% bovine serum albumin and labelled using rabbit anti-IRF9 antibody and donkey anti-rabbit antibody (Alexa Fluor 647). The cell membrane and nucleus were defined using WGA (Alexa Fluor 488) and DAPI. The image was acquired using the Zeiss LSM 980 Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope at the Africa Microscopy Initiative (AMI) Imaging Centre, University of Cape Town, South Africa. The image was further processed using ImageJ software as follows: red channel: enhance contrast: 0%, brightness and contrast (minimum and maximum displayed values: 4000 and 40000), green channel: enhance contrast: 1%, brightness and contrast (minimum and maximum displayed values: 3000 and 20000), and blue channel: enhance contrast: 0.25%, brightness and contrast (minimum and maximum displayed values: 20 and 20000). The scale bar was set using voxel size: 0.0706 x 0.0706 x 1 micron3 and resolution: 14.1661 pixels per micron.
Research career so far: I am a postdoctoral researcher and a lecturer in molecular cell biology at the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology in Ghana. Cryptolepine is an alkaloid in the medicinal plant Cryptolepis sanguinolenta. During my PhD research, we revealed the molecular mechanisms through which cryptolepine modulates type 1 interferon response, inhibits hepatoma cell growth and suppresses the hepatitis B virus replication. We showed that cryptolepine and Nibima (herbal preparation from C. sanguinolenta for managing malaria in Ghana) inhibit hepatitis B virus replication; thus, Nibima and other herbal drugs containing cryptolepine could be studied extensively for managing chronic hepatitis B virus infection in resource-limited regions since over 80% of people in these regions depend on herbal medicine for their primary healthcare needs. Managing chronic hepatitis B virus infection with cheaper herbal drugs will make the management of this infection accessible, reducing the future burden of hepatitis B virus-associated liver cancer in Africa.
Current research: With an academic and research background in immunology and molecular cell biology, I am currently focused on unravelling the triggers of hepatitis B virus-mediated liver cancer among Africans and identifying therapeutic targets. I am also exploring the area of malaria research, focusing on discovering natural products from Africa blocking malaria parasite transmission. As an early-career researcher, I am open to research training and collaborations.
Favourite imaging technique: I am captivated by live imaging using the Zeiss LSM 980 Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope.
What are you most excited about in microscopy? I am excited about live imaging and tracking immune signalling complexes in live cells.
You can read more about Seth’s experience at the AMI Imaging Center here: https://focalplane.biologists.com/2024/11/15/a-journey-of-a-novice-in-immunofluorescence-assay/


 (12 votes, average: 1.00 out of 1)
(12 votes, average: 1.00 out of 1)