Imaging spotlight: u-Segment3D
Posted by FocalPlane, on 11 December 2025
In this paper highlight, we learn about u-Segment3D, a software framework developed by Felix Zhou and Gaudenz Danuser and colleagues.
Can you briefly describe your new software?
U-Segment3D is a software framework to optimally piece together independent 2D slice-by-slice cell segmentations of a 3D volume image from three orthogonal angles, x-y, x-z and y-z into a single consensus 3D cell segmentation. Critically, we showed using first-principles to reason how the piecing together is optimal, and demonstrated that it performs on-par or even superior to native 3D cell segmentation models. Thus, u-segment3D is universally applicable. Best of all, as u-Segment3D only requires instance segmentation masks, you can use it with any 2D segmentation method and even use different 2D segmentation models for x-y, x-z and y-z slices to account for imaging resolution differences.
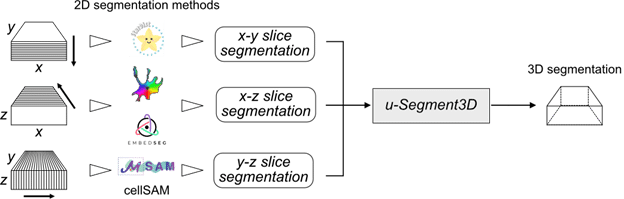
How has u-Segment3D been used so far?
We have been using it to greatly simplify the segmentation of 3D cells imaged with confocal and light-sheet microscopes in isolation under timelapse or densely packed in spheroids, cleared tissue and whole slide biopsies. We pretty much use it for everything we need segmenting in 3D. u-Segment3D is particularly useful in our research for segmenting the fine details of cell surface morphology. These high-frequency structures are rarely annotated for segmentation and therefore not captured by standard deep learning, but u-Segment3D allows recovery of these as postprocessing operations by leveraging classical methods of label diffusion and guided filtering.
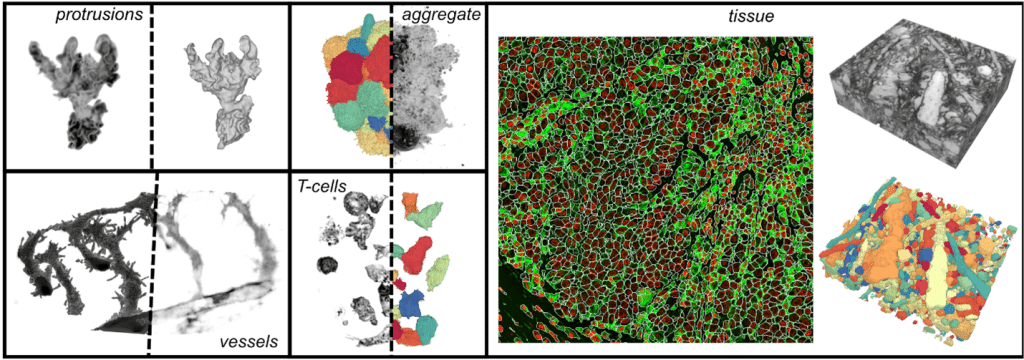
Who/what else could u-Segment3D be useful for?
Segmentation is a key first step for morphometric analysis of 3D objects. The key bottleneck has been in obtaining accurate manual 3D segmentations which has been time-consuming, potentially ambiguous to annotate, and biased to the annotator. Since our method solves the general problem of reconstructing the 3D shape from its orthogonal 2D slice decomposition, we anticipate u-Segment3D to be widely applicable for segmenting any 3D object from any modality such as medical imaging. Now, a good 2D segmentation model is also a good 3D segmentation model – two for the price of one!
What do researchers need to implement u-Segment3D?
Users will need to install the u-Segment3D Python library through the python package index, PyPI. Installation instructions, example scripts and datasets to get started are all provided through our GitHub repository, https://github.com/DanuserLab/u-segment3D. We have also developed a graphical user interface (GUI) to help run u-Segment3D. The GUI is MATLAB-based and is part of the larger u-Quantify suite developed by the Danuser Lab. For those interested, we held a recent workshop for microscopy core facility managers to use this suite of tools, see https://cellularsignaltransduction.org/workshop-2024 Session 3 for lecture notes.
What are the plans for further development?
We hope to develop more comprehensive documentation and will add more examples and features based on community interest and feedback.
Where can people find more information?
You can read our Nature Methods paper, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02887-w which goes in detail to the methodology and presents many applications including segmentation using less than three orthogonal views.
Further news and updates to the software will be disseminated on GitHub, https://github.com/DanuserLab/u-segment3D


 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)